Protect the browser and internet settings from unwanted software
When you download torrent clients, add-ons, and other programs from suspicious sites that distribute pirated content, unwanted programs may be installed on your computer without your knowledge. They aren't viruses, but they can make your browser slower, install additional toolbars without your consent, and redirect you to fraudulent, phishing, or ad pages.
Dangers of unwanted software
- Run Notepad as an administrator (to do this, right-click the program shortcut and select Run as administrator).
- Open the C:\WINDOWS\system32\drivers\etc\hosts file in Notepad.
- Delete all lines except 127.0.0.1 localhost from the file and save the changes.
- Click the menu button in the browser and select the extensions menu item (depending on the browser, it may be called Additions, Additional tools, Extensions, or Add-ons).
- Remove strange extensions.
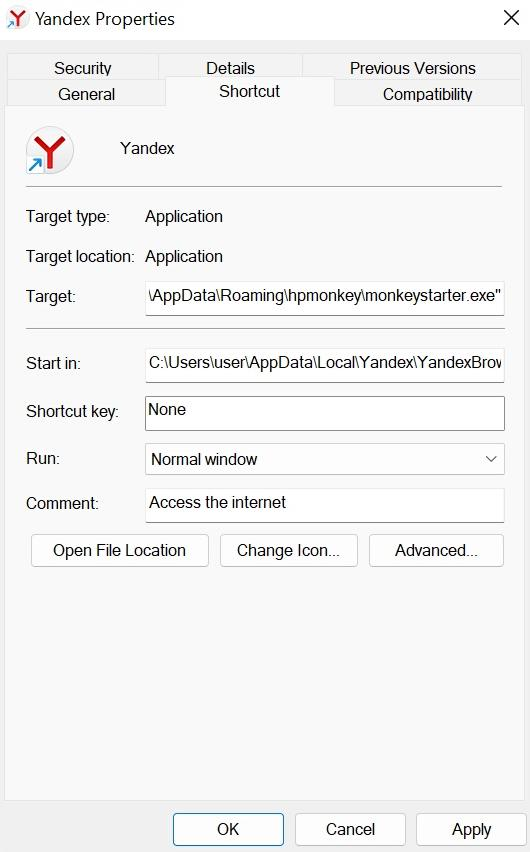
Right-click the shortcut and select Properties.
Make sure that the Target line only contains the path to the browser's executable file.
Example:C:\Program Files\Google\Chrome\Application\chrome.exeIf the Target line includes a path to an unknown file after a space, delete it and click OK.
Example:C:\Program Files\Google\Chrome\Application\chrome.exe load-and-launch-app=C:\Users\user\AppData\Local\Google\Chrome\UserData\Default\def_apps\ipcleopmlacobpjligchhkpongdjlfjh\35.0_0
The unwanted program adds an address of an ad site that mimics a popular internet service to the system registry. The key with the address is added to the section where licensed software is registered for autorun.
As a result, the ad site opens up every time you restart the computer.

The unwanted program is a filter driver that intercepts internet traffic to display intrusive and shocking ads in the browser, open ad tabs, redirect you to unwanted sites, and steal your personal data.
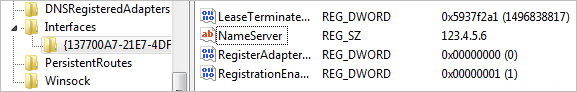
The unwanted program changes the DNS settings.
When the user opens a webpage, the browser usually sends a request specifying the domain to a special DNS server, and the server responds with the domain's IP address.
Unwanted software changes the DNS server address in the system settings. As a result, all requests are sent to another server, which redirects the user to fraudulent, phishing, or ad pages.
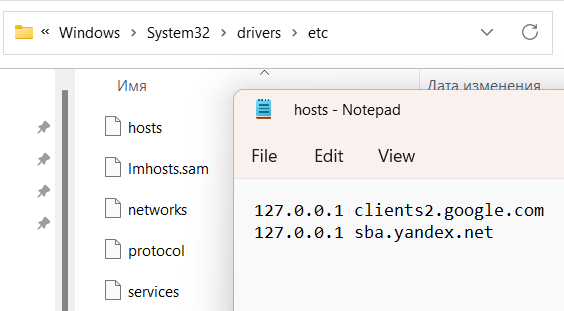
The hosts system file, which is stored in the C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc folder, contains a list of site domain addresses and their corresponding IP address.
Malware can add wrong addresses to the hosts file, blocking access to popular sites, redirecting you to phishing pages, or disabling browser security features.
If you use Windows, here's what you can do to cure your device:
The program secretly installs malicious extensions that open ad tabs in the browser, show intrusive and shocking ads, or steal your personal data.
Antiviruses are bad at recognizing malicious extensions. This is because all extensions work inside the browser and don't affect the computer's operating system.
It's best to install extensions from Opera Add-ons or Chrome Web Store, where they're tested for malware.
To check extensions that are installed in browsers:
The unwanted program runs every time the infected computer is turned on and monitors applications. When the user opens a browser, malware inserts its code into the browser process to redirect them to ad or phishing pages, change the default search settings, and steal their personal data.
The unwanted program changes the browser launch shortcut, adding new parameters (most often, a site address) or launching another app instead of the browser. As a result, ad pages open at every launch.
To check the shortcut properties:
How to remove unwanted software
Check the system with the Yandex Rescue Tool antivirus utility.
- Install the utility
- Note. If you use Yandex Browser, you don't need to download and install the utility. If a threat is detected, a “Malware detected” warning appears in the browser window. To launch the utility, click Start scan and cleanup.
- To get a system cleaning utility, contact support.
- In the response email, you'll receive a link to download the utility. Follow this link.
- Open the saved executable file rescue_tool.exe and click Run.
By launching the utility, you agree to its Terms of Usage.
- Start cleanup
-
- In the System cleanup utility, click Start scan.
- Allow the utility to make changes to the device.
- If unwanted software is detected, the system offers to remove them. To view the list of detected programs, click the Scan report link.
- To complete the cleanup, go to the Potentially unwanted applications found window and click Remove. To remove some programs completely, you may need to restart the computer.
If unwanted software wasn't found or some malicious programs weren't removed, run the cleanup again.
If you repeated the cleanup and no unwanted programs were detected or removed but you're sure that the computer is at risk, try using free antiviruses or contact support.